IDENTIFYING COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
Competitive Advantage:
- A feature of a product or service on which customers place a greater value than they do on similar offerings from competitors.
- But, it is temporary because competitors keep duplicate the strategies.
- Then, the company should start the new competitive advantage.
- buyer power
- supplier power
- threat of substitute products or services
- threats of new entrants
- rivalry among existing companies
Three Generic Strategies
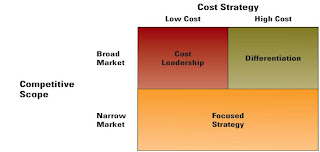
COST LEADERSHIP
- becoming a low-cost producer in the industry allows the company to lower prices to customers.
- competitors with higher cost cannot afford to compete with the low-cost leader on price.
- create competitive advantage by distinguishing their products on one or more features important to their customers.
- unique features or benefits may justify prices differences and/or stimulate demand.
- target to a niche market
- concentrates on either cost leadership or differentiation.
- supply chain - a chain or series of processes that adds value to product and service for customer.
- add value to its products and services that support a profit margin for the firm.

No comments:
Post a Comment